April is Sexually Transmitted Awareness Month

This April, in honor of STI Awareness Month, take some time to learn about sexually transmitted infections (STIs). Anyone who is sexually active can get an STI, so why not learn more about them and how to minimize your exposure to STIs and take care of your sexual health.
Can I get an STI from oral sex?

Can someone get a sexually transmitted infection (STI) from oral sex? Yes. Many STIs, including chlamydia, gonorrhea and syphilis, can be transmitted through oral sex.
Can HIV be transmitted by fingering?

I know this is probably stupid but, I was fingering someone last Saturday night and I had a hangnail on my finger. Could I have gotten HIV?
Nongonococcal Urethritis (NGU)

Nongonococcal urethritis (NGU) is an infection of the urethra that is not caused by gonorrhea. You can get NGU by touching your mouth, penis, vagina, or anus, to someone else’s penis, vagina, or anus (who has NGU).
Statistics on STIs — Chlamydia, Gonorrhea, and Syphilis
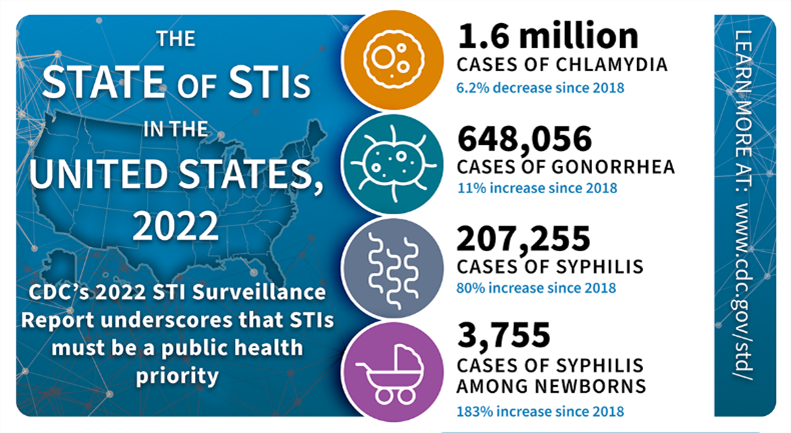
There were 2.5 million cases of chlamydia, gonorrhea, and syphilis reported in the United States in 2022. Rates of gonorrhea and chlamydia remain high, and rates of syphilis have gone up an alarming 80% since 2018.
Your Safer Sex Toolbox — It’s more than just condoms

Being sexual with someone carries risks—risk of rejection, of unintended pregnancy, of contracting an STI, or even a simple cold. But being sexual also provides physical, emotional and spiritual benefits.
What are scabies?

Scabies is similar to pubic lice, but the bugs are too small to be seen. The bugs dig under the skin. A health care provider can tell if you have scabies by looking at the burrows (often in a zigzag or “S” pattern) or rash.
Sexually Transmitted Infections (STIs) — Five Things You Need to Know

Sexually transmitted infections (STIs), affect people of all ages, backgrounds, and from all walks of life. As the name suggests, STIs are usually are passed on through sex—vaginal, oral or anal.
Crabs (a.k.a. public lice) are a curable STI

Crabs are tiny little blood-sucking bugs (lice) that live in pubic hair and cause a lot of itching. You get crabs by touching or just being close to someone who already has them. Even if you don’t have sex, you can get crabs or give them to someone else.
Mgen: The STI You’ve (Probably) Never HeardMgen:

Mycoplasma genitalium, or Mgen, was first identified in 1981. It is a bacterium that can infect the reproductive tract and is passed on through sexual contact.
